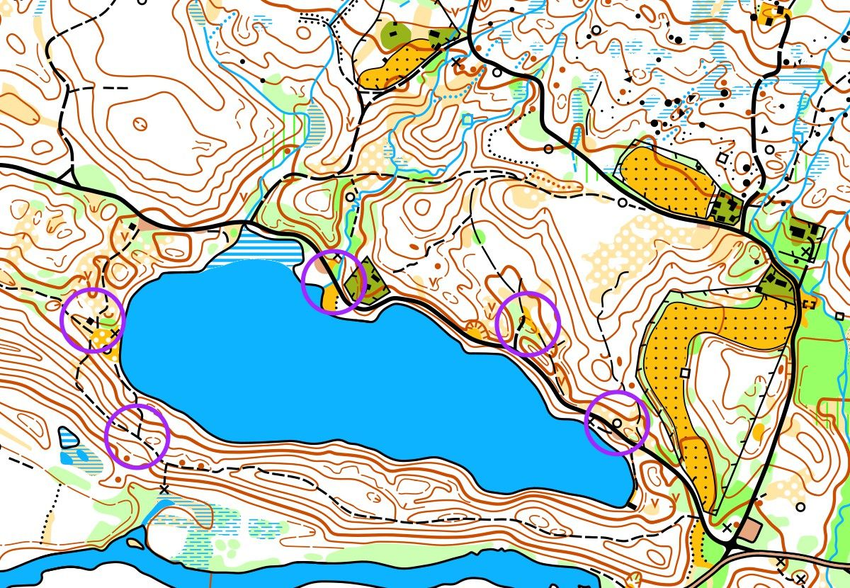
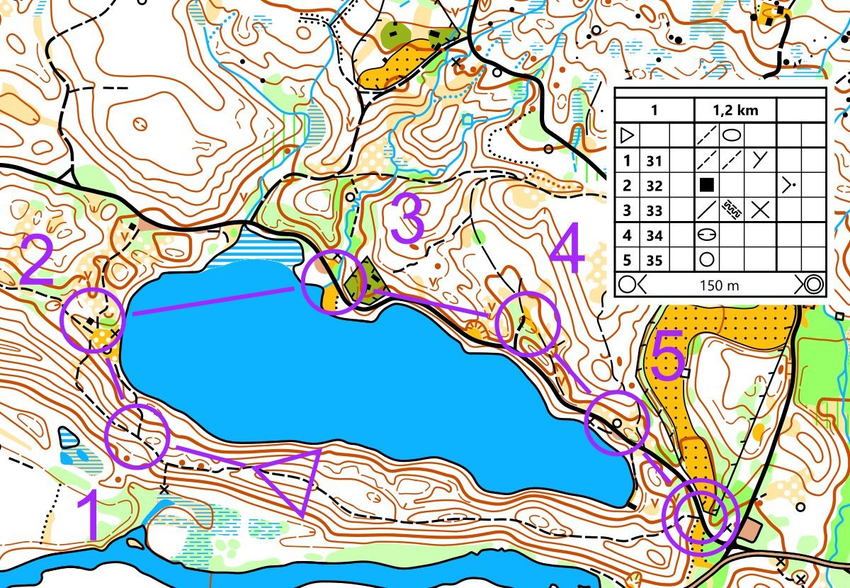
The map often includes descriptions of control points (legend). This description provides information about CP, such as CP number, CP details, and its location in relation to the terrain. CP descriptions may be marked with special symbols or words.
Routes - checkpoints and other symbols on the map
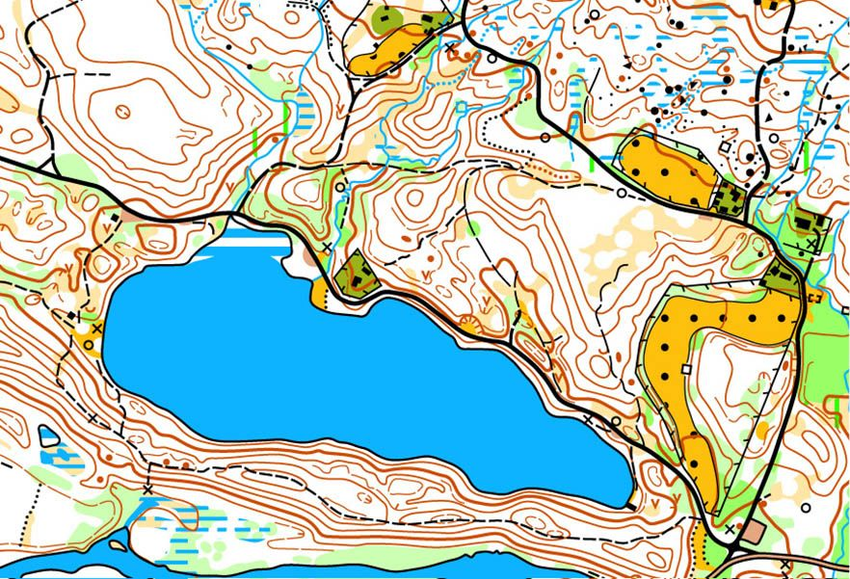
The locations to find are called checkpoints (hereinafter - CP) and are marked with a circle on the map. In the center of the CP circle, there is a detail that is easily visible in the area. At this place, a CP prism is hanging.
Map and Terrain Comparison
The start of the orienteering course is marked with a triangle, and the finish with a double circle. Lines are drawn between the control points to easily see the order in which they should be found. Note that each control point has a number. You start from the start, find control point 1, then control point 2, control point 3, control point 4, control point 5 and finally reach the finish.

Scale
Forest map scales are typically 1:7,500, 1:10,000, 1:15,000. Sprint map scales are typically 1:4,000. Schoolyard map scales are typically 1:1,000 and 1:2,500. Indoor map scales are typically from 1:100 to 1:500.
Scale always indicated in the map
The map always includes information about the scale. There is often a certain ruler, indicating the scale, called a scale bar. Using it, you can directly determine how much the distance on the map corresponds to reality. Imagine if the scale were 1:1. Then the map would have to be as large as the entire area!

TIP
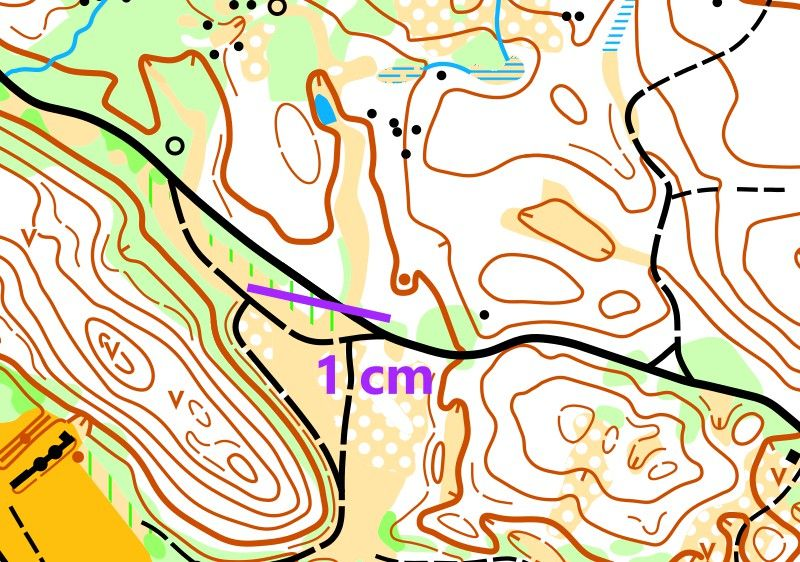
Remove the last two zeros at the end of the scale and you will always get the number of meters. In this map, the scale is 1:1000. 1 cm on the map corresponds to 1000 cm in the field, i.e., 10 meters.
Practice evaluating distances
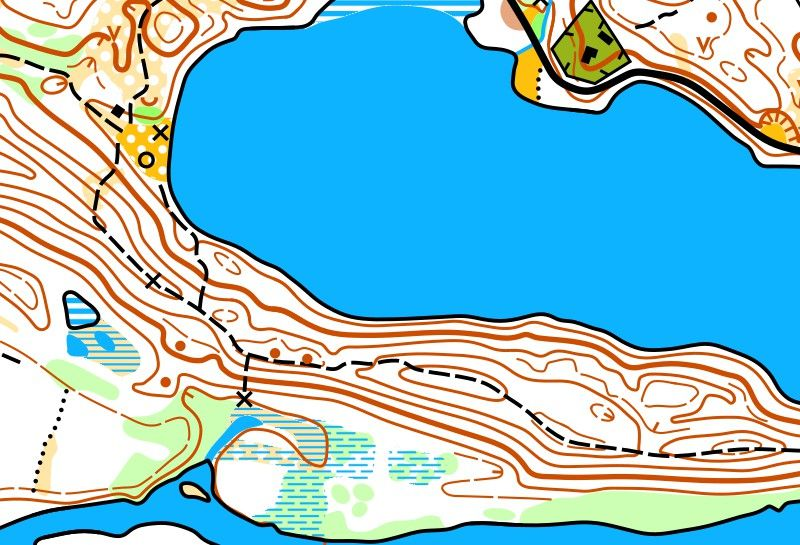
Map scale, recalculated to meters on the ground, measured in a straight (air) line. The terrain can be quite steep. Therefore, the distance in the area is always longer than measured on the map.
Develop your eyes to gauge distances so that you can easily determine whether an object is 20, 50, or 100 meters away. Do you assume what these distances are?
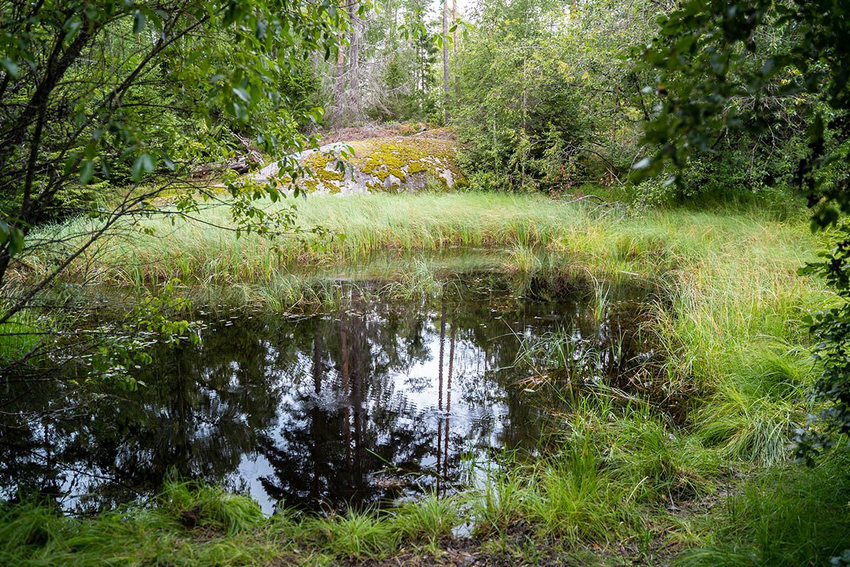
How far is the top of the small hill beyond the water from where you are standing?

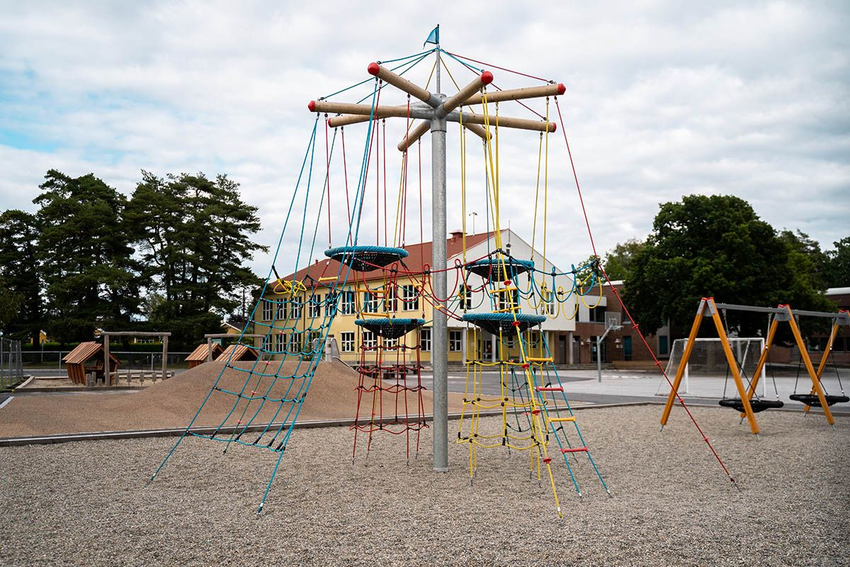
How far is the school building from where you are standing?

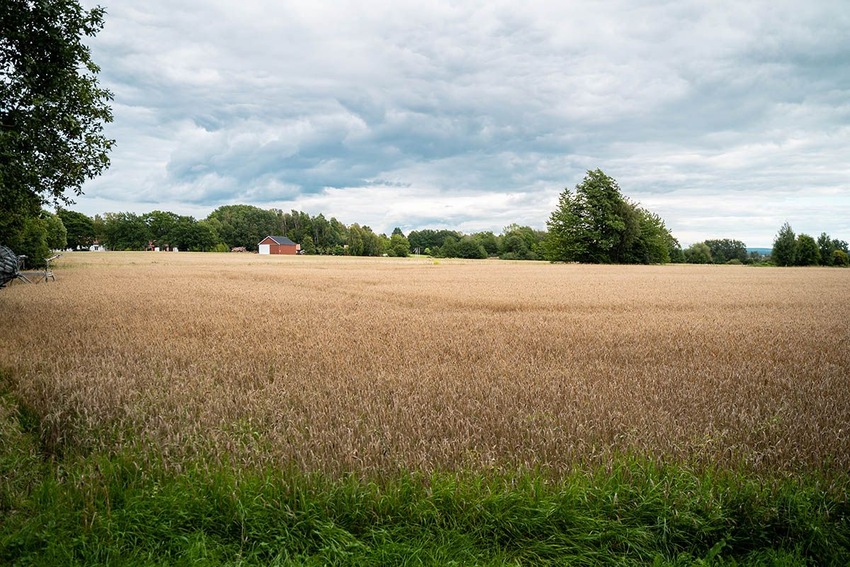
How far is the red barn on the other side of the field from where you are standing?

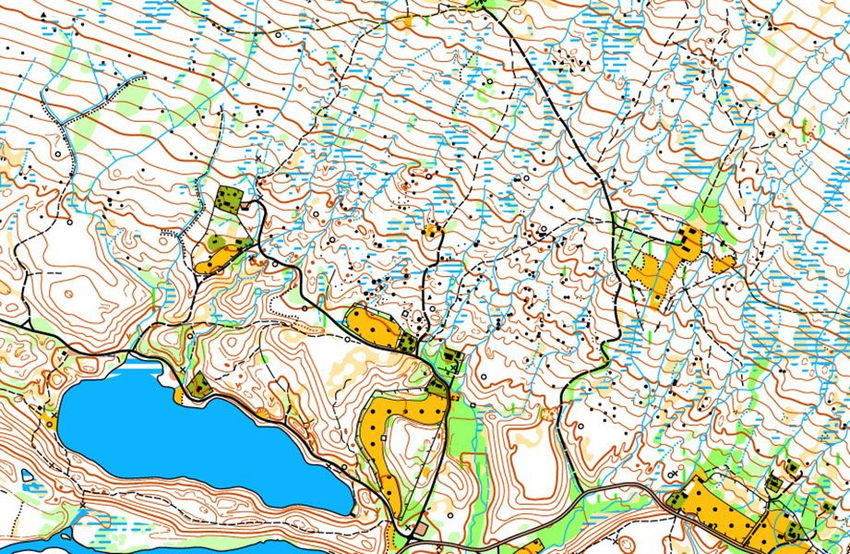
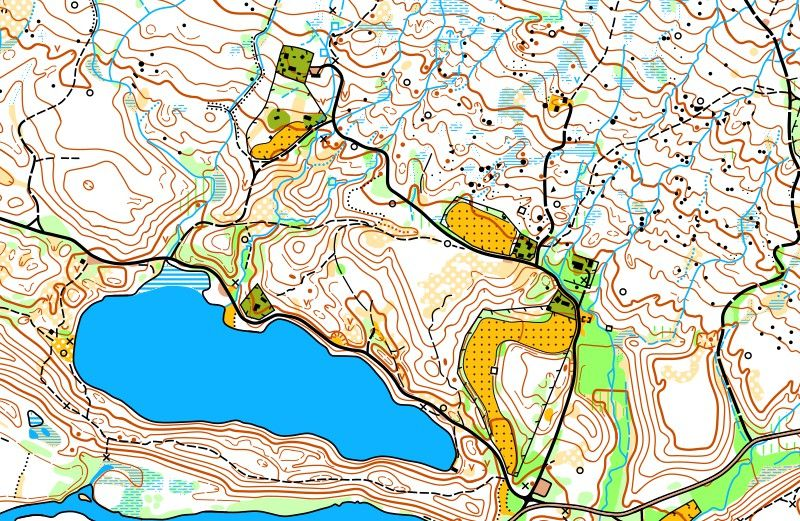
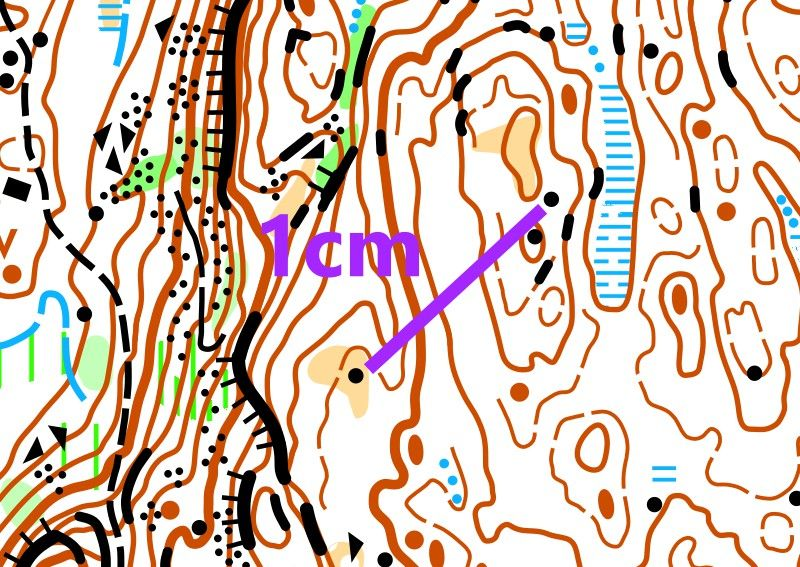
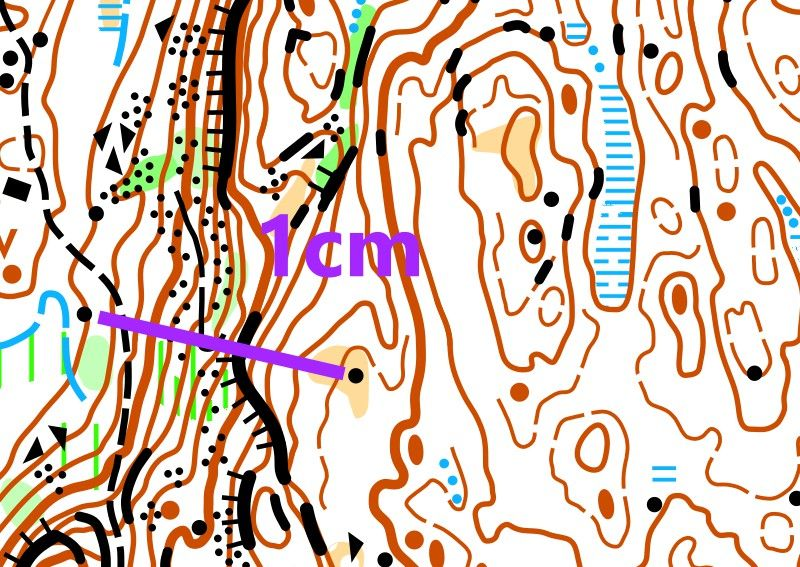
To orientate well, you must learn to assess distances in a location. Here you see two maps of the same area with different scales. The scale of the first one is 1:10,000, the second one is 1:5,000.

When the scale is 1:10,000, 1 cm on the map represents 100 meters in reality. However, when the scale is 1:5,000, 1 cm on the map only represents 50 meters in reality. If you have a map with a scale of 1:5,000, distances will appear much shorter than on a map with a scale of 1:10,000.